排序
排序
# 912. 排序数组 (opens new window)
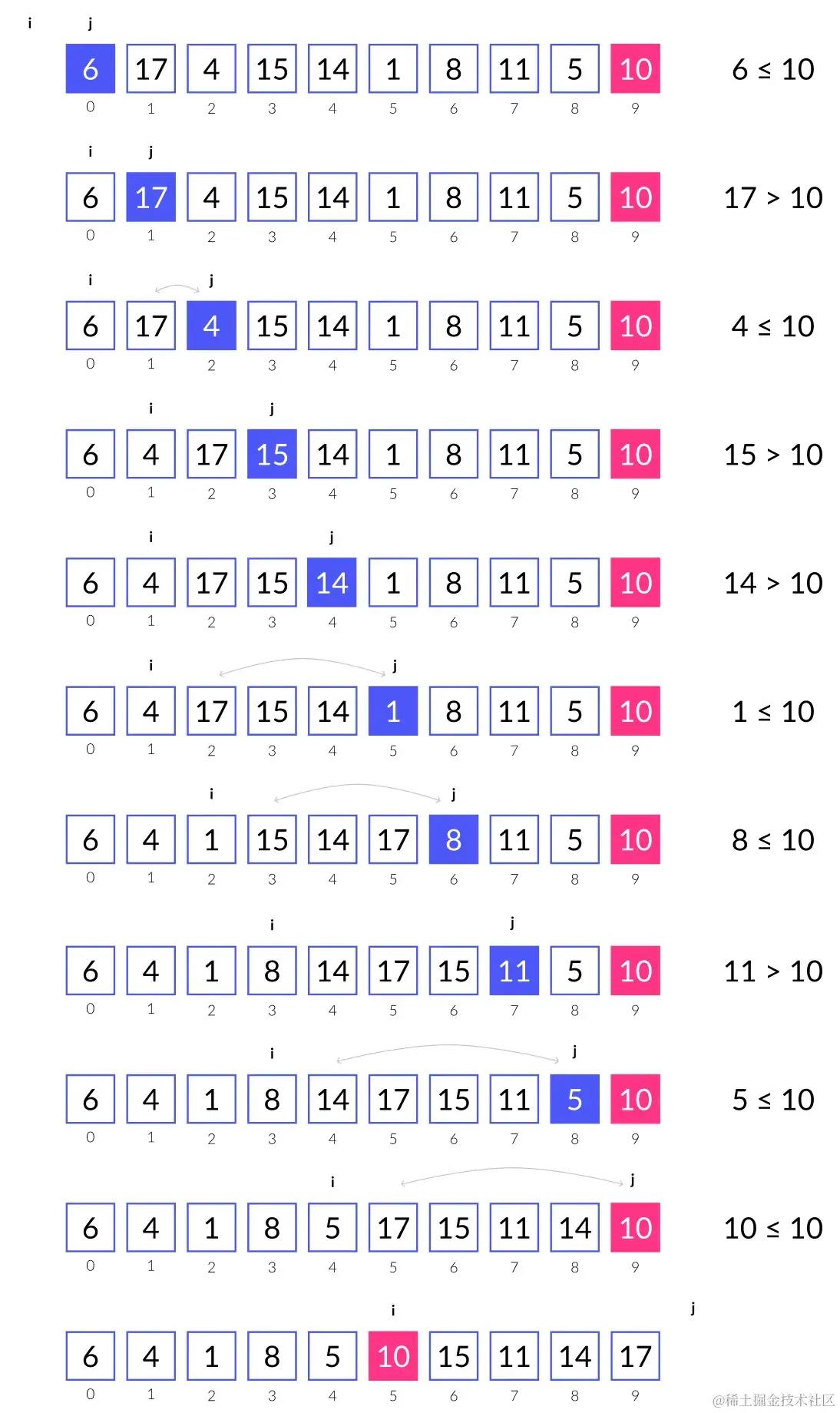
# 冒泡排序
class Solution {
int[] nums;
public int[] sortArray(int[] nums) {
this.nums = nums;
int n = nums.length;
for(int j=n-1;j>0;j--){
for(int i=0;i<j;i++){
if(nums[i]>nums[i+1]){
swap(i,i+1);
}
}
}
return nums;
}
void swap(int l,int r){
int tmp = nums[l];
nums[l] = nums[r];
nums[r] = tmp;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 快速排序
时间复杂度:O(nlogn)~O(n^2)
当前区间内选择一个轴,区间中所有比轴小的数放到比轴的左边,大的放到轴右边;
最理想情况,选取的轴刚好在这个区间的中位数,就与归并排序一致;
最差情况,每次选取的轴刚好是最大值或最小值,每轮排序都需要进行n次比较,每次时间复杂度为O(n),总时间复杂度为O(n^2);
class Solution {
int[] nums;
public int[] sortArray(int[] nums) {
this.nums = nums;
if(nums==null || nums.length<2)
return nums;
shuffle();
quickSort(0,nums.length-1);
return nums;
}
void quickSort(int l,int r){
if(l>r) return ;
int p = partition(l,r);
quickSort(l,p-1);
quickSort(p+1,r);
}
int partition(int l,int r){
int base = nums[r];
int i = l;
for(int j=l;j<r;j++){
if(nums[j]<base){
swap(i,j);
i++;
}
}
swap(i,r);
return i;
}
void shuffle(){
Random rand = new Random();
int n = nums.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int r = i+rand.nextInt(n-i);
swap(i,r);
}
}
void swap(int l,int r){
int tmp = nums[l];
nums[l] = nums[r];
nums[r] = tmp;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
# 归并排序
时间复杂度:O(nlogn),稳定
分治思想,每次将区间对半划分,直到长度为1;然后将相邻两个子区间进行合并;
每一层的时间复杂度为O(n),共有logn层,总时间复杂度为O(nlogn);
以最右边的数为轴:
class Solution {
int[] nums;
public int[] sortArray(int[] nums) {
this.nums = nums;
sort(0,nums.length-1);
return nums;
}
void sort(int l,int r){
if(l==r)
return ;
int mid = (l+r)>>>1;
sort(l,mid);
sort(mid+1,r);
merge(l,mid,r);
}
void merge(int l,int mid,int r){
int[] tmp = new int[r-l+1];
int i=0;
int p1=l,p2=mid+1;
while(p1<=mid && p2<=r)
tmp[i++] = nums[p1]<=nums[p2]?nums[p1++]:nums[p2++];
while(p1<=mid)
tmp[i++] = nums[p1++];
while(p2<=r)
tmp[i++] = nums[p2++];
for(i=0;i<tmp.length;i++){
nums[l+i] = tmp[i];
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# 堆排序
提前知道数组,从最后一个元素下调heapify;(小数下调)
如果不知道所有数字,每个数字给出后上调heapInsert;(大树往上移)
void heapInsert(int[] arr, int index) { while (arr[index] > arr[(index - 1) / 2]) { swap(arr, index, (index - 1) / 2); index = (index - 1) / 2; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
class Solution {
public int[] sortArray(int[] nums) {
if(nums==null || nums.length<2)
return nums;
// 每次heapify,第一个元素为最大元素;
for(int i=nums.length-1;i>=0;i--)
heapify(nums,i,nums.length);
int heapSize = nums.length;
swap(nums,0,--heapSize);// 最大的元素到了最后,就不是大根堆了
// 重新调整大根堆,每次将最大元素移动至最后,堆大小-1
while(heapSize>0){
heapify(nums,0,heapSize);
swap(nums,0,--heapSize);
}
return nums;
}
void heapify(int[] nums,int index,int heapSize){
int l = index*2+1;
while(l<heapSize){
// 节点不一定有右子树,越界判断,将左右子树最大值下标给largest;
int largest = l+1<heapSize && nums[l]<nums[l+1] ? l+1:l;
// 若最大值大于父节点,进行交换,并继续向下传导,index=largest;
if(nums[largest]<=nums[index])
break;
else{
swap(nums,largest,index);
index = largest;
l = index*2+1;
}
}
}
void swap(int[] nums,int i,int j){
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
# 快速排序
# 75. 颜色分类 (opens new window)
参考:75. 颜色分类 - 力扣(LeetCode) (opens new window)
循环不变量写法一:
nums中:
- [0,l) = 0 保证初始化为空,l=0,遍历到 0时先交换再加
- [l,i] = 1
- [r,n-1] = 2 保证初始化为空,r=n,遍历到 2时先减再交换
循环终止条件 i==r,循环可以继续条件:i<r;
如果首尾都是2,r一直左移到不是2的位置,再与i交换;
class Solution {
public void sortColors(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
if(n<2) return ;
int l=0,r=n;
int i=0;
while(i<r){
if(nums[i]==0){
swap(nums,i,l);
l++;
i++;
}else if(nums[i]==1){
i++;
}else{
r--;
swap(nums,i,r);
}
}
}
void swap(int[] nums,int l,int r){
int tmp = nums[l];
nums[l] = nums[r];
nums[r] = tmp;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
循环不变量写法二:
nums中:
- [0,l] = 0 保证初始化为空,l=-1,遍历到 0时先加再交换
- (l,i) = 1
- (r,n-1] = 2 保证初始化为空,r=n-1,遍历到 2时先交换再减
循环终止条件 i==r+1,循环继续条件:i<=r
class Solution {
public void sortColors(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
if(n<2) return ;
int l=-1,r=n-1;
int i=0;
while(i<=r){
if(nums[i]==0){
l++;
swap(nums,i,l);
i++;
}else if(nums[i]==1){
i++;
}else{
swap(nums,i,r);
r--;
}
}
}
void swap(int[] nums,int l,int r){
int tmp = nums[l];
nums[l] = nums[r];
nums[r] = tmp;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# 384. 打乱数组 (opens new window)
class Solution {
int[] nums;
int[] init;
public Solution(int[] nums) {
this.nums = nums;
this.init = new int[nums.length];
System.arraycopy(nums,0,init,0,nums.length);
}
public int[] reset() {
System.arraycopy(init,0,nums,0,nums.length);
return nums;
}
public int[] shuffle() {
Random random = new Random();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
int r = i+random.nextInt(nums.length-i);
swap(i,r);
}
return nums;
}
void swap(int i,int j){
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# 215. 数组中的第K个最大元素 (opens new window)
方法一:快排
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
shuffle(nums);
int l=0,r=nums.length-1;
k = nums.length-k;
while(l<=r){
int p = partition(nums,l,r);
if(p<k) l = p+1;
else if(p>k) r = p-1;
else return nums[p];
}
return -1;
}
int partition(int[] nums,int l,int r){
int base = nums[r];
int i = l;
for(int j=l;j<r;j++){
if(nums[j]<base){
swap(nums,i,j);
i++;
}
}
swap(nums,i,r);
return i;
}
void shuffle(int[] nums){
Random random = new Random();
int n = nums.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int r = i+random.nextInt(n-i);
swap(nums,i,r);
}
}
void swap(int[] nums,int l,int r){
int tmp = nums[l];
nums[l] = nums[r];
nums[r] = tmp;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
方法二:优先级队列
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
for(int num:nums){
pq.offer(num);
if(pq.size()>k){
pq.poll();
}
}
return pq.peek();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 归并排序
# 88. 合并两个有序数组 (opens new window)
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int[] arr1 = new int[m];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
arr1[i] = nums1[i];
int[] arr2 = nums2;
int i=0,j=0;
int p = 0;
while(i<m && j<n)
nums1[p++] = arr1[i]>arr2[j]?arr2[j++]:arr1[i++];
while(i<m)
nums1[p++] = arr1[i++];
while(j<n)
nums1[p++] = arr2[j++];
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# 4. 寻找两个正序数组的中位数 (opens new window)
class Solution {
public double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int m = nums1.length,n = nums2.length;
int[] nums = new int[m+n];
int i=0,j=0,k=0;
while(i<m && j<n){
nums[k++] = nums1[i]<=nums2[j]?nums1[i++]:nums2[j++];
}
while(i<m){
nums[k++] = nums1[i++];
}
while(j<n){
nums[k++] = nums2[j++];
}
if(k%2==0){
return (nums[k/2-1]+nums[k/2])/2.0;
}else{
return nums[k/2];
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# 327. 区间和的个数 (opens new window)
# 315. 计算右侧小于当前元素的个数 (opens new window)
class Solution {
Pair[] tmp;
int[] cnt;// 记录比自己小的个数
public List<Integer> countSmaller(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
this.cnt = new int[n];
this.tmp = new Pair[n];
Pair[] pair = new Pair[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
pair[i] = new Pair(nums[i],i);
}
sort(pair,0,n-1);
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
for(int e:cnt){
ret.add(e);
}
return ret;
}
void sort(Pair[] pair,int l,int r){
if(l==r) return ;
int mid = l+(r-l)/2;
sort(pair,l,mid);
sort(pair,mid+1,r);
merge(pair,l,mid,r);
}
void merge(Pair[] pair,int l,int mid,int r){
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++){
tmp[i] = pair[i];
}
int i=l;
int j=mid+1;
for(int p=l;p<=r;p++){
if(i==mid+1){
pair[p] = tmp[j++];
}else if(j==r+1){
pair[p] = tmp[i++];
cnt[pair[p].idx] += j-mid-1;
}else if(tmp[i].val>tmp[j].val){
pair[p] = tmp[j++];
}else{ // 5,8(i) 6,10(j)
pair[p] = tmp[i++];
cnt[pair[p].idx] += j-mid-1;
}
}
}
class Pair{
int val;
int idx;
Pair(int val,int idx){
this.val = val;
this.idx = idx;
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
# 493. 翻转对 (opens new window)
# 169. 多数元素 (opens new window)
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
return rec(nums,0,nums.length-1);
}
// 返回众数
int rec(int[] nums,int l,int r){
// size为1的数组,该元素就是众数
if(l==r)
return nums[l];
int mid = (l+r)>>>1;
int leftHalf = rec(nums,l,mid);
int rightHalf = rec(nums,mid+1,r);
if(leftHalf == rightHalf)
return leftHalf;
int leftCount = countInRange(nums,leftHalf,l,r);
int rightCount = countInRange(nums,rightHalf,l,r);
return leftCount>rightCount?leftHalf:rightHalf;
}
int countInRange(int[] nums,int num,int l,int r){
int cnt = 0;
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++){
if(nums[i]==num){
cnt++;
}
}
return cnt;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28