容器与Bean
容器与Bean
# 容器
# BeanFactory
ApplicationContext的父接口,核心容器,ApplicationContext的实现都组合了BeanFactory的功能;
功能:表面只有getBean(),实际控制反转,依赖注入,Bean的生命周期都由其实现类提供;
通过反射查看它的成员变量 singletonObjects,内部包含了所有的单例 Bean:
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(A01.class, args); ...... Field singletonObjects = DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.class.getDeclaredField("singletonObjects"); singletonObjects.setAccessible(true); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory(); Map<String, Object> map = (Map<String, Object>) singletonObjects.get(beanFactory); map.entrySet().stream().filter(e -> e.getKey().startsWith("component")) .forEach(e -> { System.out.println(e.getKey() + "=" + e.getValue()); });1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
容器实现:DefaultListableBeanFactory
负责控制反转和依赖注入功能;
public class TestBeanFactory { public static void main(String[] args) { DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); // bean 的定义(class, scope, 初始化, 销毁) AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(Config.class).setScope("singleton").getBeanDefinition(); beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("config", beanDefinition); /** * BeanFactory 后处理器 */ // 如何获取@Configuration这个Bean下的所有Bean? // 给 BeanFactory 添加一些常用的后处理器 AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(beanFactory); // BeanFactory 后处理器主要功能,补充了一些 bean 定义 beanFactory.getBeansOfType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class).values().forEach(beanFactoryPostProcessor -> { beanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); }); /** * Bean 后处理器 */ // 如何找到依赖注入的Bean? // Bean 后处理器, 针对 bean 的生命周期的各个阶段提供扩展, 例如 @Autowired @Resource ... beanFactory.getBeansOfType(BeanPostProcessor.class).values().forEach(beanPostProcessor->{ System.out.println(">>>>>>>>"+beanPostProcessor); // 添加BeanFactory与 Bean后处理器 之间的联系 beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(beanPostProcessor); }); for(String name:beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()){ System.out.println(name); } // 所有的bean先创建BeanDefinition,真正调用才创建实例,单例对象建议一开始就创建好 beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(); // 准备好所有单例 System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> "); System.out.println(beanFactory.getBean(Bean1.class).getBean2()); } @Configuration static class Config { @Bean public Bean1 bean1() { return new Bean1(); } @Bean public Bean2 bean2(){ return new Bean2(); } } static class Bean1{ private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Bean1.class); public Bean1() { log.debug("构造 Bean1()"); } @Autowired private Bean2 bean2; public Bean2 getBean2() { return bean2; } } static class Bean2{ private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Bean2.class); public Bean2() { log.debug("构造 Bean2()"); } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
# ApplicationContext
BeanFactory 的子接口。它扩展了 BeanFactory 接口的功能,如:
国际化;
通配符方式获取一组 Resource 资源;
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(A01.class, args); ...... Resource[] resources = context.getResources("classpath*:META-INF/spring.factories"); for (Resource resource : resources) { System.out.println(resource); }1
2
3
4
5
6整合 Environment 环境(能通过它获取各种来源的配置信息);
context.getEnvironment().getProperty("java_home")1事件发布与监听,实现组件之间的解耦;
事件
UserRegisteredEvent:public class UserRegisteredEvent extends ApplicationEvent { public UserRegisteredEvent(Object source) { super(source); } }1
2
3
4
5Bean1负责用户注册然后发送通知:
@Component public class Component1 { private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Component1.class); @Autowired private ApplicationEventPublisher context; public void register(){ log.debug("用户注册"); context.publishEvent(new UserRegisteredEvent(this)); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13Bean2:
@Component public class Component2 { private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Component2.class); @EventListener public void test(UserRegisteredEvent event){ log.debug("{}",event); log.debug("发送短信"); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10启动类:
@SpringBootApplication public class A01 { private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(A01.class); public static void main(String[] args) { ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(A01.class,args); context.getBean(Component1.class).register(); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
容器实现:
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,从类路径查找 XML 配置文件,创建容器(旧);
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext,从磁盘路径查找 XML 配置文件,创建容器(旧);
XmlWebApplicationContext,传统 SSM 整合时,基于 XML 配置文件的容器(旧);
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext,传统 SSM 整合时,基于 java 配置类的容器(旧);
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,Spring boot 中非 web 环境容器(新);
private static void testAnnotationConfigApplicationContext() { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class); for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) { System.out.println(name); } System.out.println(context.getBean(Bean2.class).getBean1()); } @Configuration static class Config{ @Bean public Bean1 bean1(){ return new Bean1(); } @Bean public Bean2 bean2(Bean1 bean1){ Bean2 bean2 = new Bean2(); bean2.setBean1(bean1); return bean2; } } static class Bean1{} static class Bean2{ private Bean1 bean1; public Bean1 getBean1() { return bean1; } public void setBean1(Bean1 bean1) { this.bean1 = bean1; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext,Spring boot 中 servlet web 环境容器(新);
private static void testAnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext() { AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext(WebConfig.class); for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) { System.out.println(name); } } @Configuration static class WebConfig{ @Bean public ServletWebServerFactory servletWebServerFactory(){ return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory(); } @Bean public DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet() { return new DispatcherServlet(); } // 将Servlet注册到tomcat服务器上 @Bean public DispatcherServletRegistrationBean registrationBean(DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet) { return new DispatcherServletRegistrationBean(dispatcherServlet, "/"); } @Bean("/hello") public Controller controller1() { return (request, response) -> { response.getWriter().print("hello"); return null; }; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext,Spring boot 中 reactive web 环境容器(新);
# Bean
# 生命周期
graph LR
创建 --> 依赖注入
依赖注入 --> 初始化
初始化 --> 可用
可用 --> 销毁
2
3
4
5
6
创建:根据 bean 的构造方法或者工厂方法来创建 bean 实例对象;
依赖注入:根据 @Autowired,@Value 或其它一些手段,为 bean 的成员变量填充值、建立关系;
初始化:回调各种 Aware 接口,调用对象的各种初始化方法;
销毁:在容器关闭时,会销毁所有单例对象(即调用它们的销毁方法);
prototype 对象也能够销毁,不过需要容器这边主动调用;
# Bean增强
实例化前后的增强:
postProcessBeforeInstantiation
这里返回的对象若不为 null 会替换掉原本的 bean,并且仅会走 postProcessAfterInitialization 流程;
postProcessAfterInstantiation
这里如果返回 false 会跳过依赖注入阶段;
依赖注入前的增强:
postProcessProperties
如 @Autowired、@Value、@Resource ;
初始化前后的增强:
postProcessBeforeInitialization
这里返回的对象会替换掉原本的 bean,如 @PostConstruct、@ConfigurationProperties;
postProcessAfterInitialization
这里返回的对象会替换掉原本的 bean,如代理增强;
销毁之前的增强:
postProcessBeforeDestruction
如 @PreDestroy ;
# Bean后处理器
Spring自带Bean后处理器:
- AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 解析 @Autowired 与 @Value
- CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 解析 @Resource、@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy
- ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor 解析 @ConfigurationProperties
- ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver 负责获取 @Value 的值,解析 @Qualifier、泛型、@Lazy 等
# BeanFactory后处理器
Spring自带BeanFactory后处理器:
- ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 可以解析
- @ComponentScan
- @Bean
- @Import
- @ImportResource
- MapperScannerConfigurer 可以解析
- Mapper 接口
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
context.registerBean("config", Config.class);
context.registerBean(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class); // 这个Bean 用于解析 @ComponentScan @Bean @Import @ImportResource
context.registerBean(MapperScannerConfigurer.class, bd -> { // 这个Bean 用于解析 @MapperScanner Mybatis用
bd.getPropertyValues().add("basePackage", "com.Nreal.IOC.A3.mapper");
});
context.refresh();
for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
自定义BeanFactory后处理器:
Config Bean:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.Nreal.IOC.A3.component")
public class Config {
@Bean
public Bean1 bean1() {
return new Bean1();
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean(DataSource dataSource) {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
return sqlSessionFactoryBean;
}
@Bean(initMethod = "init")
public DruidDataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("root");
return dataSource;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
将@ComponentScan的Bean加入容器;
public class ComponentScanPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor { @Override // context.refresh public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException { } // 将@CompponetScan 中包里的带有@Component的Bean注册到容器里 @Override public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry beanFactory) throws BeansException { try { ComponentScan componentScan = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(Config.class, ComponentScan.class); if (componentScan != null) { for (String p : componentScan.basePackages()) { System.out.println(p); // com.itheima.a05.component -> classpath*:com/itheima/a05/component/**/*.class String path = "classpath*:" + p.replace(".", "/") + "/**/*.class"; //System.out.println(path); CachingMetadataReaderFactory factory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory(); Resource[] resources = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources(path);// context.getResources(path) AnnotationBeanNameGenerator generator = new AnnotationBeanNameGenerator(); for (Resource resource : resources) { // System.out.println(resource); MetadataReader reader = factory.getMetadataReader(resource); // System.out.println("类名:" + reader.getClassMetadata().getClassName()); AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = reader.getAnnotationMetadata(); // System.out.println("是否加了 @Component:" + annotationMetadata.hasAnnotation(Component.class.getName()));//Component // System.out.println("是否加了 @Component 派生:" + annotationMetadata.hasMetaAnnotation(Component.class.getName()));//Controller if (annotationMetadata.hasAnnotation(Component.class.getName()) || annotationMetadata.hasMetaAnnotation(Component.class.getName())) { AbstractBeanDefinition bd = BeanDefinitionBuilder .genericBeanDefinition(reader.getClassMetadata().getClassName()) .getBeanDefinition(); String name = generator.generateBeanName(bd, beanFactory); beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(name, bd); } } } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43将@Configuration下的@Bean加入容器;
public class AtBeanPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor { @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException { } @Override public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry beanFactory) throws BeansException { try { CachingMetadataReaderFactory factory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory(); //MetadataReader不走类加载,效率比反射高 MetadataReader reader = factory.getMetadataReader(new ClassPathResource("com/Nreal/IOC/A3/Config.class")); Set<MethodMetadata> methods = reader.getAnnotationMetadata().getAnnotatedMethods(Bean.class.getName()); for (MethodMetadata method : methods) { System.out.println(method); String initMethod = method.getAnnotationAttributes(Bean.class.getName()).get("initMethod").toString(); BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(); // 调用的是@Config下的@Bean builder.setFactoryMethodOnBean(method.getMethodName(), "config"); // 指定自动装配模式,否则解析不了DataSource builder.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR); if (initMethod.length() > 0) { builder.setInitMethodName(initMethod); } AbstractBeanDefinition bd = builder.getBeanDefinition(); beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(method.getMethodName(), bd); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32测试:
context.registerBean(ComponentScanPostProcessor.class); // 解析 @ComponentScan context.registerBean(AtBeanPostProcessor.class); // 解析 @Bean1
2扫描到的Bean:
config com.Nreal.IOC.A3.ComponentScanPostProcessor com.Nreal.IOC.A3.AtBeanPostProcessor bean2 bean3 bean1 sqlSessionFactoryBean dataSource
# Aware&InitializingBean
Aware接口:
- BeanNameAware 注入 bean 的名字;
- BeanFactoryAware 注入 BeanFactory 容器;
- ApplicationContextAware 注入 ApplicationContext 容器;
- EmbeddedValueResolverAware ${};
为什么需要 Aware?
@Autowired 的解析需要用到 bean后处理器,属于扩展功能;
而 Aware接口属于内置功能,不加任何扩展,Spring 就能识别;
案例:
public class MyBean implements BeanNameAware, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyBean.class);
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
log.debug("当前bean " + this + " 名字叫:" + name);
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
log.debug("当前bean " + this + " 初始化");
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
log.debug("当前bean " + this + " 容器是:" + applicationContext);
}
// 没有Bean后处理器,下两个方法不生效
@Autowired
public void NeedBeanPostProcessor(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
log.debug("当前bean " + this + " 使用@Autowired 容器是:" + applicationContext);
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
log.debug("当前bean " + this + " 使用@PostConstruct 初始化");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
public class TestAware {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TestAware.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
context.registerBean("myBean", MyBean.class);
// bean后处理器
context.registerBean(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
context.registerBean(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
context.registerBean(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
context.refresh();
context.close();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
配置类@Autowired失效
@Configuration
public class MyConfig1 {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyConfig1.class);
@Autowired
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
log.debug("注入 ApplicationContext");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
log.debug("初始化");
}
@Bean // beanFactory 后处理器
public BeanFactoryPostProcessor processor1() {
return beanFactory -> {
log.debug("执行 processor1");
};
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
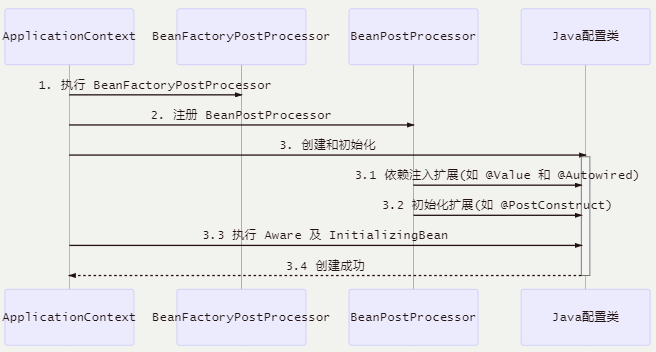
只会执行 processor1,@Autowired与@PostConstruct全部失效;
原因:使用了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor,调用这个方法,必须提前创建 Java配置类,而此时BeanPostProcessor还未准备好,导致@Autowired等注解失效;
Java 配置类不包含 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的情况:
包含 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的情况:
解决方法:使用Aware与InitializingBean接口;
@Configuration public class MyConfig2 implements InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware { private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyConfig2.class); @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { log.debug("初始化"); } @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { log.debug("注入 ApplicationContext"); } @Bean // beanFactory 后处理器 public BeanFactoryPostProcessor processor2() { return beanFactory -> { log.debug("执行 processor2"); }; } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21